Landing gears play a crucial role in the safe and efficient operation of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Different types are needed for different categorizes of UAVs and special changes should be made to adapt to various terrains. In this section, we will introduce all kinds of landing gears and the requirements to select them.
Generally speaking, landing gears should be selected according to the three main categories of UAVs:
- fixed-wing
- rotary-wing
- hybrid types
Fixed-wing:
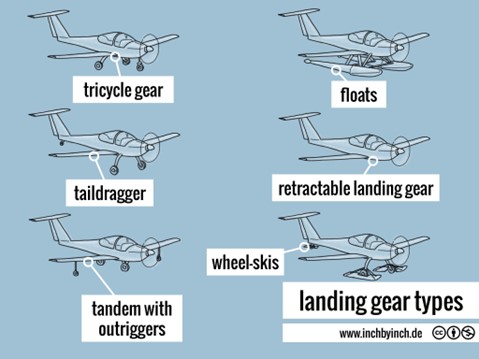
– Tricycle Landing Gear:
- Directional Stability:
Tricycle gear provides better directional stability on the ground, especially during taxiing and takeoff. The nose wheel helps to keep the aircraft aligned with the runway, reducing the risk of ground loops and making it easier to control.
- Easier Ground Handling:
With a nose wheel, the UAV is more stable and easier to handle on the ground. It allows for smoother and more controlled movements, which can be particularly beneficial during pre-flight checks and post-flight operations.
- Improved Visibility:
In manned aircraft, tricycle gear improves the pilot’s visibility over the nose of the aircraft. While this is less relevant for UAVs, it can still be advantageous for onboard sensors or cameras that need an unobstructed view of the forward direction.
- Reduced Risk of Tip-Over:
Tricycle gear reduces the risk of the UAV tipping over when parked or during ground operations. The lower center of gravity and the nose-down attitude help to keep the aircraft stable, even in windy conditions.
- Better Takeoff and Landing Performance:
During takeoff, the nose-high attitude provided by tricycle gear can improve lift generation, potentially allowing for shorter takeoff distances. On landing, the nose wheel touches down after the main wheels, which can provide a smoother transition from flight to the ground.
- Adaptability to Different Surfaces:
Tricycle gear can often handle a wider range of surface types and conditions, including rough or uneven terrain, without the same risk of tipping as a taildragger configuration.
- Integration with Autonomous Systems:
Tricycle gear can be more compatible with autonomous taxiing and ground navigation systems, as the inherent stability and ease of control make it simpler to program and operate autonomously.
– Taildragger Landing Gear:
It consists of two main wheels in the front and a single, small tail wheel at the rear.
- Simplified Design:
For small or lightweight drones, a taildragger landing gear can simplify the structural design. With only one point of support at the tail, it may be simpler and lighter than a tricycle gear.
- Stability on Ground:
When the drone is stationary on the ground, a taildragger gear keeps the aircraft in a level or slightly nose-up position. This can improve stability during ground operations, especially during pre-takeoff preparations.
- Landing Characteristics:
During landing, the main wheels touch down first, followed by the tail wheel. This sequence helps control the aircraft to decelerate smoothly and reduces the impact force on the nose section.
- Shorter Airstrips:
Due to the increased angle of attack during takeoff and landing, taildraggers can access shorter airstrips compared to nose-wheel planes.
- Cost-Effectiveness:
For smaller-scale projects with limited budgets, using a simpler taildragger landing gear system can reduce manufacturing costs while still providing the necessary functionality.
- Specific Application Requirements:
Some specialized drones, such as those designed for low-altitude flights or operations in challenging terrain, might prefer a taildragger design due to specific operational requirements.
– Quadricycle Landing Gear:
Quadricycle landing gears are a configuration that consists of four main landing gear units roughly equal in size and mounted along the fuselage. This type of landing gear is similar to bicycle gear but with four main units instead of two. Here are some characteristics of quadricycle landing gears.
- Even Weight Distribution:
Quadricycle gears are designed to distribute the aircraft’s weight more evenly across four points, which can be beneficial for larger aircraft or those with a wide load distribution.
- Cargo Accessibility:
One of the significant advantages of quadricycle gear is that it allows the plane’s floor to be very close to the ground, facilitating easier loading and unloading of cargo.
- Sensitivity to Roll and Crosswinds:
Like bicycle gear, quadricycle undercarriages require a very flat attitude during takeoff and landing and are sensitive to roll, crosswinds, and proper alignment with the runway.
- Higher Drag:
This configuration generates more drag than bicycle gear due to the additional wheels and landing gear structures, which can impact the aircraft’s performance.
- Complex Retraction System:
Since quadricycle gears have multiple units, their retraction systems are more complex and require more space within the aircraft’s fuselage.
- Stability:
Quadricycle landing gears can provide stability during ground operations, especially for aircraft with a wide wingspan or large cargo holds.
- Common in Cargo Aircraft:
This type of landing gear is sometimes used on cargo planes where ease of loading and unloading is essential. A well-known example is the B-52 bomber, which employs a variation of the quadricycle and bicycle arrangements with four main gear plus two small outriggers near the wingtips.
– Tandem Landing Gear:
This type has two main landing gears, one under each wing, and no nose landing gear, used when the center of gravity of the UAV is towards the rear.
- Aerodynamic Efficiency:
Tandem gear can offer improved aerodynamic efficiency due to the streamlined undercarriage, which is beneficial for high-altitude or long-endurance flights.
- Wing Flexibility:
This configuration often allows for very flexible wings, which can be advantageous for certain aircraft designs, such as sailplanes, where high wing flexibility is desired for soaring.
- Narrow Body Aircraft:
Tandem landing gears are well-suited for aircraft with a narrow fuselage, as they help maintain a compact and streamlined shape.
- Ground Handling:
Tandem gear can make ground handling more challenging due to the risk of the aircraft tipping to one side, especially during taxiing. Some aircraft may have small outrigger wheels or skids on the wingtips to mitigate this.
- Retraction:
In some cases, tandem landing gears can be retractable, which involves a more complex retraction mechanism compared to tricycle gear, as the gear needs to be stowed within the narrow fuselage.
- Operational Limitations:
Tandem landing gear may not be suitable for all types of operations, especially those that require frequent or rough landings, as the undercarriage may not provide the same level of shock absorption as other configurations.
– Floats (Amphibious Gear):
For UAVs that need to operate over water, floats can be used instead of wheels. These allow the UAV to take off from and land on water. Some floats are designed to work on both water and land, making the UAV amphibious.
Rotary-wing:
– Skid Landing Gear:
This type of landing gears are straightforward in design, typically consisting of a pair of parallel bars that run along the length of the aircraft, allowing it to land on a variety of surfaces without the need for wheels.
- Lightweight:
The skids are usually made from lightweight materials like aluminum or carbon fiber, and attached to the UAV’s frame.
- Ease of Maintenance:
Skids are low-maintenance and can be easily replaced if they become damaged.
- Cost-Effectiveness:
Due to their simple design and use of standard materials, skid landing gears are often less expensive than more complex landing gear systems.
- Versatility:
Skids can be used on a variety of surfaces, although very soft or uneven ground may require additional protection or a different landing gear solution.
- Energy Absorption:
Skids can absorb some impact energy during landing, reducing the stress on the UAV’s airframe and components.
- Aerodynamic Considerations:
While skids do add some drag, their streamlined profile and small frontal area minimize this impact, especially on smaller UAVs.
- Customizability:
Skids can be easily customized or modified to fit specific UAV designs or to accommodate additional equipment.
- Suitability for Small UAVs:
Skid landing gears are particularly suited to small UAVs where complexity and weight are critical factors.
– Multi-Rotor Landing Gear:
Designed for UAVs with multiple arms and rotors attached to them, Multi-Rotor Landing Gear allows for vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) capabilities and hovering. The landing gear itself usually attaches to all the rotor’s bottom allowing for a lowere center of gravity.
– Innovative Designs:
There are ongoing developments in adaptive and robotic landing gear that can adjust to complex terrains, such as those inspired by bird claws or other biological structures, to enhance stability in various environments.
Hybrid UAV (VTOLs) :
– Skid Landing Gear: (see “-Skid Landing Gear” above)
Whether or not to make landing gears retractable should also be carefully considered, as this decision can greatly influence the fuselage design of your UAV:
Yes:
- High-Speed Flight:
For fixed-wing UAVs that operate at higher speeds, retractable landing gears can significantly reduce drag, enhancing the vehicle’s performance and efficiency.
- Long-Endurance Missions:
When a UAV is designed for long flights with minimal drag, retractable landing gears can help conserve energy and extend the flight duration.
- Aerodynamic Considerations:
In instances where aerodynamics play a critical role, such as in high-altitude or high-performance UAVs, retractable landing gears help maintain a smooth undercarriage, reducing the overall drag coefficient.
- Performance-Oriented UAVs:
For UAVs where takeoff and landing are less frequent but speed and agility are prioritized, such as in military or advanced surveillance applications, retractable landing gears can be beneficial.
No:
- Simple or Cost-Effective UAVs:
For basic or cost-sensitive UAVs where the complexity and additional cost of a retractable landing gear system are not justified, fixed landing gears may be more suitable.
- Lightweight Requirements:
In cases where every gram of weight is critical, such as in racing or small recreational UAVs, the added weight and complexity of retractable landing gears may be undesirable.
- Limited Space:
UAVs with limited internal space may not have the room needed for a retractable landing gear system, as it requires space for the gear to retract and stow.
- VTOL UAVs:
Vertical Take-Off and Landing UAVs, such as multi-rotors, often do not require retractable landing gears since they take off and land vertically and do not rely on forward speed for lift.
- Rough Field Operations:
For UAVs that frequently operate from unprepared or rough terrain, the additional mechanical complexity of retractable landing gears may increase the risk of damage or malfunction.
- Redundancy and Safety:
In situations where reliability and safety are paramount, such as in cargo transport UAVs, fixed landing gears might be preferred for their simplicity and reliability.